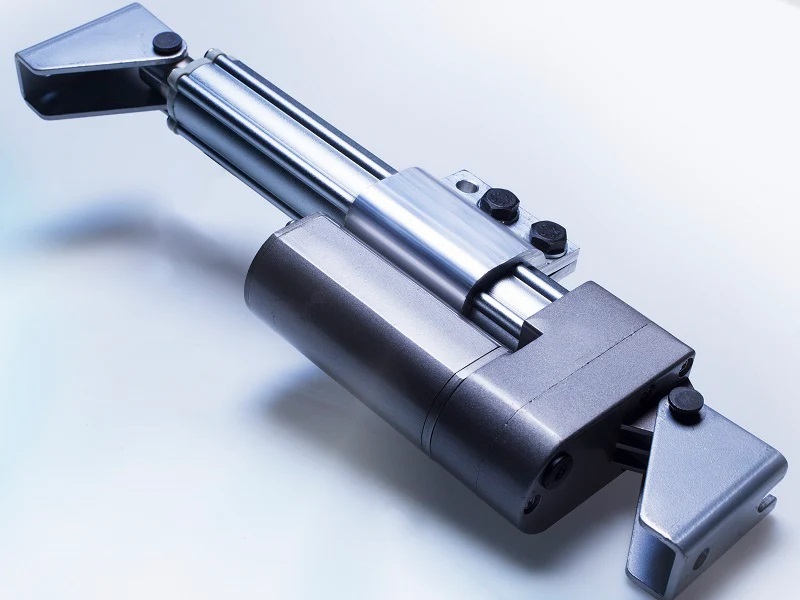
Do you need a compact and versatile tool for your next automation project? Look no further than the 12 volt linear actuator. These workhorse devices translate electrical power into precise linear motion, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. Whether you are a seasoned engineer or just starting your automation journey, this article will equip you with the knowledge to harness the power of linear actuators for your projects.
The landscape of automation is brimming with possibilities and demands a diverse toolbox of reliable components. Within this arsenal, you can see a versatile and powerful solution, namely the linear actuator 12 volt. Discover how it can become the cornerstone of your automation endeavors.
What is a 12 Volt Linear Actuator?
A 12-volt linear actuator is a self-contained unit consisting of a 12V DC motor, a gearbox, a lead screw (or threaded rod), and a control system. When an electrical current from a 12-volt power source energizes the motor, it rotates a shaft. This rotation is then translated into linear motion through the gearbox, which increases the torque (rotational force) of the motor.
The lead screw threaded like a screw but linear in function, converts this rotational force into a pushing or pulling action along its length, creating the stroke of the actuator. The control system governs the direction and distance of the devices’s movement.
Advantages of Using a 12 Volt Linear Actuator
The true beauty of these actuators lies in their advantages:
Precision in Movement
They offer exceptional precision in movement, making them ideal for applications requiring controlled linear motion. The lead screw mechanism ensures consistent and repeatable stroke lengths, crucial for tasks demanding accuracy.
Compact Size and Easy Installation
Their small size allows for integration into various projects, while many models come with pre-drilled mounting holes for straightforward installation. This compact design minimizes space constraints and allows for creative freedom in your automation endeavors.
Energy Efficiency
Operating on a low voltage (12 volts DC), these compact devices are energy-efficient, making them ideal for battery-powered applications and conscious automation projects.
Versatility and Flexibility
12V actuators are available in many configurations, with varying stroke lengths, force capacities, and speed options. It allows you to tailor the device to your specific needs, whether it controls a camera slider or automates furniture adjustments for an ergonomic workspace.
Applications in Various Industries
The potential applications of these devices are vast:
Automotive Industry
From powering automatic seat adjustments and retractable sunroofs to controlling pop-up headlights, 12V linear motors contribute to driver comfort and convenience in modern vehicles.
Robotics and Automation
They are the driving force behind many innovative robots, powering precise movements in small robots, automating tasks in assembly lines, or creating automated plant irrigation systems.
Medical Devices
Their ability to provide smooth, controlled linear motion makes these motors ideal for various medical applications that require precision and reliability:
· Physical therapy equipment. Adjustable treatment tables, automated resistance training devices, and specialized wheelchairs can utilize 12V linear actuators to enhance functionality and patient comfort.
· Diagnostic tools. Linear motors can be used in positioning equipment for X-ray machines or other diagnostic imaging systems, ensuring precise alignment for accurate results.
Home Automation
With these motors, you can automate furniture like adjustable desks or Murphy beds for a more ergonomic and space-saving environment. They allow for smooth window blinds control enabling you to set up convenient light. Their possibilities extend to creating automatic pet feeders or hidden storage compartments with pop-up mechanisms.
Other Industries
Here are some additional industries using electric motors:
· Agriculture. Automating greenhouse ventilation systems, controlling irrigation equipment, or powering automated harvesting machines.
· Manufacturing. Precise positioning of materials in assembly lines, powering conveyor belt adjustments, 12V linear motors can improve efficiency and streamline production processes.
· Furniture manufacturing. Adjustable chairs, ergonomic workstations, and automatic reclining mechanisms in couches can all be powered by the reliable force of 12-volt devices.
Choosing the Right 12 Volt Linear Actuator
When selecting the perfect option for your project, consider several key factors:
Load Capacity
It refers to the maximum weight or force the actuator can push or pull. Choose an actuator with a load capacity exceeding your project’s requirements to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature wear. For example, if you automate a heavy Murphy bed, a higher load capacity actuator would be necessary compared to one controlling a set of window blinds.
Speed and Stroke Length
Consider the desired movement speed for your project and the total distance (stroke length) the actuator needs to travel. 12V solutions come in various stroke lengths and speeds, so finding the right balance for your application is crucial.
For instance, a motor powering a camera slider might prioritize a slower, more precise movement with a shorter stroke length. An actuator adjusting a desk height might require a faster speed and a longer stroke length.
Durability and Maintenance
Assess the environment in which the actuator will operate. Some models offer weatherproof features or higher ingress protection ratings for applications exposed to moisture or dust.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
As with any mechanical or electrical device, occasional issues might arise. By understanding the most common problems and their potential solutions, you can ensure your automation system functions smoothly:
· Power supply issues. Verify the power source functions correctly and is connected to the actuator.
· Control system malfunctions. Ensure the control system (switch, remote control, or control board) works correctly and sends the appropriate signals to the actuator.
· Overload. If the actuator is not moving or struggling, check if the load it is trying to push or pull exceeds its capacity. Reduce the weight or force if necessary.
· Mechanical issues. Unusual noises or limited movement might indicate mechanical issues like a worn lead screw, lack of lubrication, or loose mounting hardware. Consult the manual for troubleshooting steps or contact the manufacturer for further assistance.
The 12-volt linear actuator has become a cornerstone of modern automation. By offering a perfect blend of precision, efficiency, and versatility, these devices empower you to breathe life into creative projects across numerous industries.