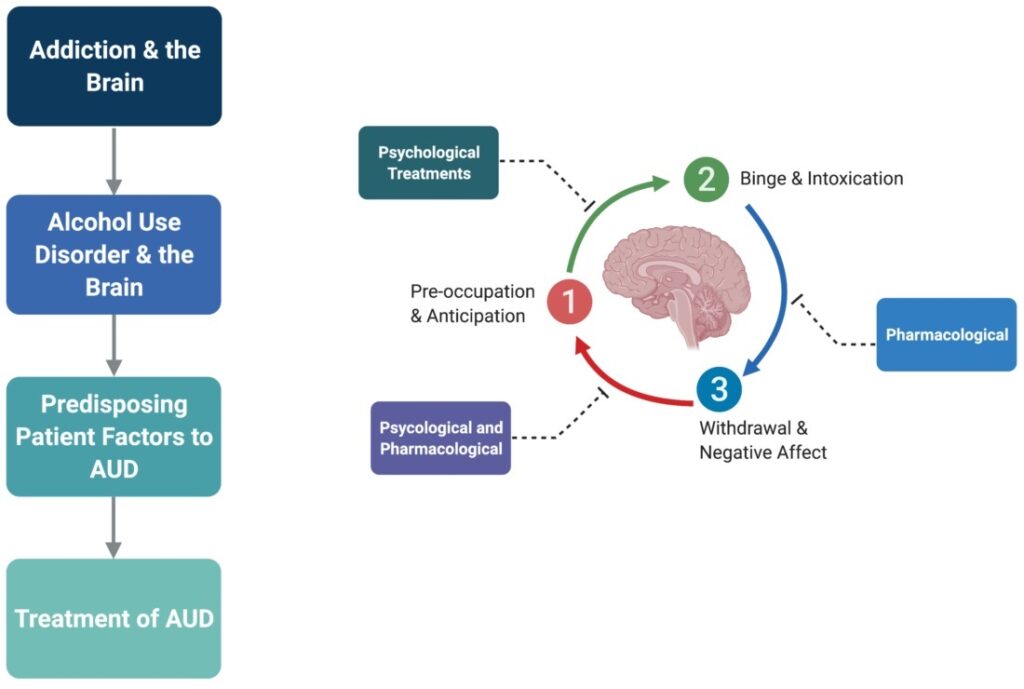
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) in adolescents is a pressing concern, given the profound impact it can have on their physical, mental, and emotional development. Early intervention and tailored alcohol user disorder treatment strategies are essential to address the unique needs of adolescents struggling with alcohol use.
Recognizing the Signs of Alcohol Use Disorder in Adolescents
Identifying AUD in adolescents can be challenging, as the signs may be subtle or mistaken for typical teenage behavior. However, early detection is crucial for effective intervention. Some common signs of AUD in adolescents include:
- Changes in Behavior: Sudden shifts in mood, increased irritability, or frequent conflicts with family and friends.
- Decline in Academic Performance: Falling grades, lack of interest in school, and increased absenteeism.
- Physical Symptoms: Unexplained injuries, frequent hangovers, or changes in weight and appetite.
- Social Changes: Withdrawing from usual activities, changing peer groups, or spending time with friends who drink.
- Secretive Behavior: Lying about whereabouts, hiding alcohol, or being unusually secretive.
Factors Contributing to Adolescent Alcohol Use
Several factors can contribute to the development of AUD in adolescents, including:
- Peer Pressure: Adolescents are highly influenced by their peers, and the desire to fit in can lead to experimenting with alcohol.
- Family Environment: Family dynamics, parental attitudes towards alcohol, and genetic predisposition can all play a role.
- Mental Health Issues: Depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders can increase the risk of alcohol use as a coping mechanism.
- Trauma and Stress: Experiencing trauma or chronic stress can lead adolescents to use alcohol to numb their emotions.
- Accessibility: Easy access to alcohol, whether at home or through social circles, can contribute to early experimentation and misuse.
Effective Strategies and Treatments for Adolescents
Family-Based Therapy: Family involvement is crucial in treating AUD in adolescents. Family-based therapies, such as Functional Family Therapy (FFT) and Multidimensional Family Therapy (MDFT), address family dynamics and improve communication. These therapies help build a supportive home environment and involve parents in the recovery process.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is effective in helping adolescents identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to alcohol use. This therapy provides coping strategies for managing stress, peer pressure, and triggers. It also helps adolescents develop healthier ways to cope with emotions.
Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET): MET focuses on enhancing an adolescent’s motivation to change their drinking behavior. This therapy helps them explore the pros and cons of alcohol use and develop a personal commitment to sobriety. MET is particularly effective in the early stages of treatment.
School-Based Programs: Integrating treatment with school-based programs ensures that adolescents receive support in their everyday environment. Programs that include counseling, peer support groups, and educational workshops can help adolescents stay on track academically and socially while addressing their alcohol use.
Support Groups for Adolescents: Peer support groups specifically designed for adolescents provide a safe space to share experiences and receive encouragement. Groups like Alateen, a part of Al-Anon Family Groups, offer support to young people affected by someone else’s drinking, helping them understand they are not alone.
Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques: Teaching adolescents mindfulness and stress reduction techniques can help them manage anxiety and emotions without turning to alcohol. Practices like mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises promote emotional regulation and resilience.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): In some cases, medication may be used to support recovery in adolescents. Medications like naltrexone can help reduce cravings and prevent relapse. However, the use of MAT in adolescents requires careful consideration and should be supervised by a healthcare professional.
Recreational and Extracurricular Activities: Encouraging adolescents to engage in recreational and extracurricular activities provides healthy outlets for their energy and emotions. Sports, arts, and community service can boost self-esteem, provide a sense of accomplishment, and reduce the risk of alcohol use.
Educational Programs for Parents and Caregivers: Educating parents and caregivers about the signs of AUD, risk factors, and effective communication strategies is essential. Providing resources and support can help them guide their children through recovery and create a healthy, alcohol-free environment at home.
Developing a Relapse Prevention Plan: Relapse prevention planning is crucial for long-term success. This plan should include strategies for identifying and managing triggers, coping with stress, and seeking support when needed. Regular follow-ups with counselors and healthcare providers can help monitor progress and adjust the plan as necessary.
Addressing Co-Occurring Disorders: Many adolescents with AUD also struggle with co-occurring mental health disorders. Integrated treatment that addresses both alcohol use and underlying mental health issues is essential for comprehensive care. Therapies that target both conditions simultaneously can lead to better outcomes.
Creating a Positive Support Network: Building a positive support network of family, friends, teachers, and counselors is vital for an adolescent’s recovery journey. This network provides encouragement, accountability, and a sense of belonging, which are crucial for maintaining sobriety.
Read More: How to regain confidence and a more youthful appearance through chin sculpting